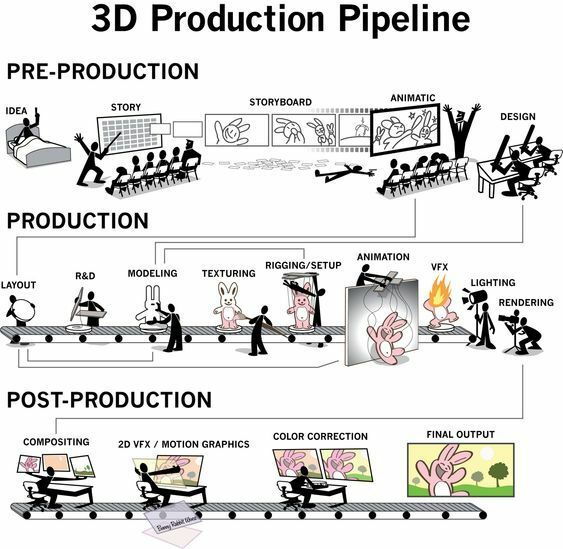
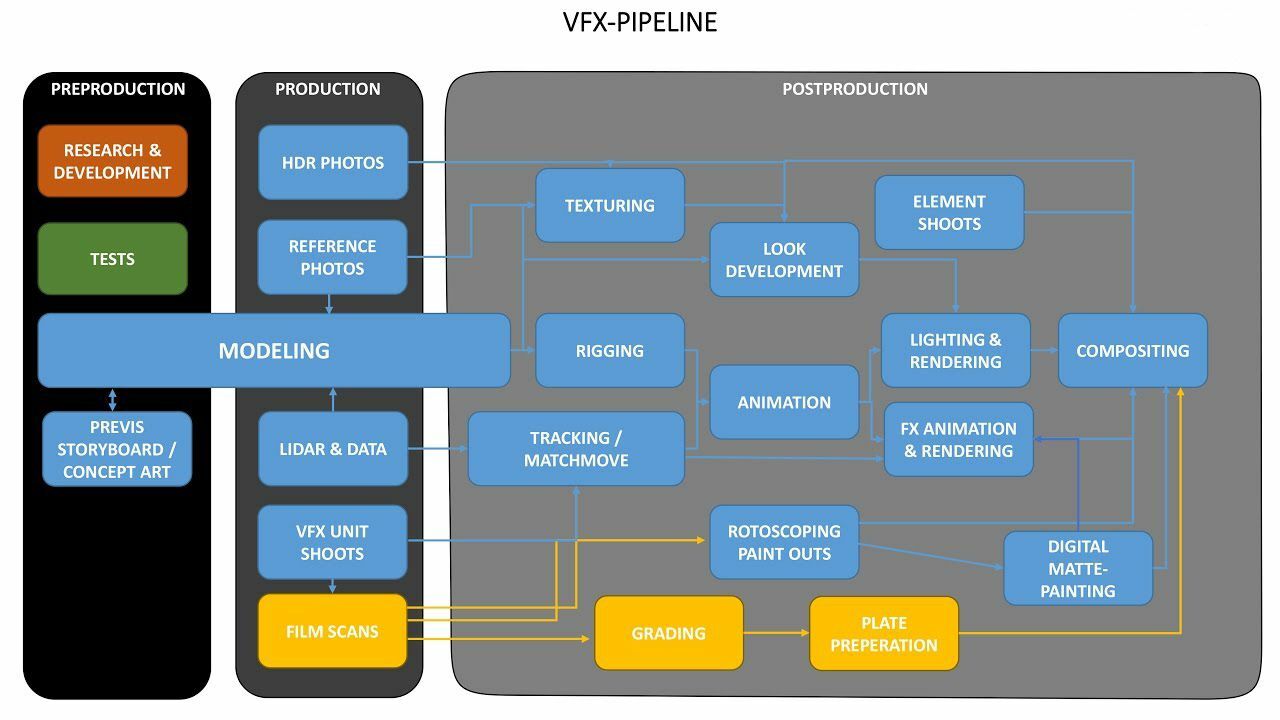
The first step in any VFX pipeline is usually research and development.
Second step is Pre-visualization. It is essentially the process of converting a storyboard and script into a 3D animated, low-quality rough draft of each VFX shot.
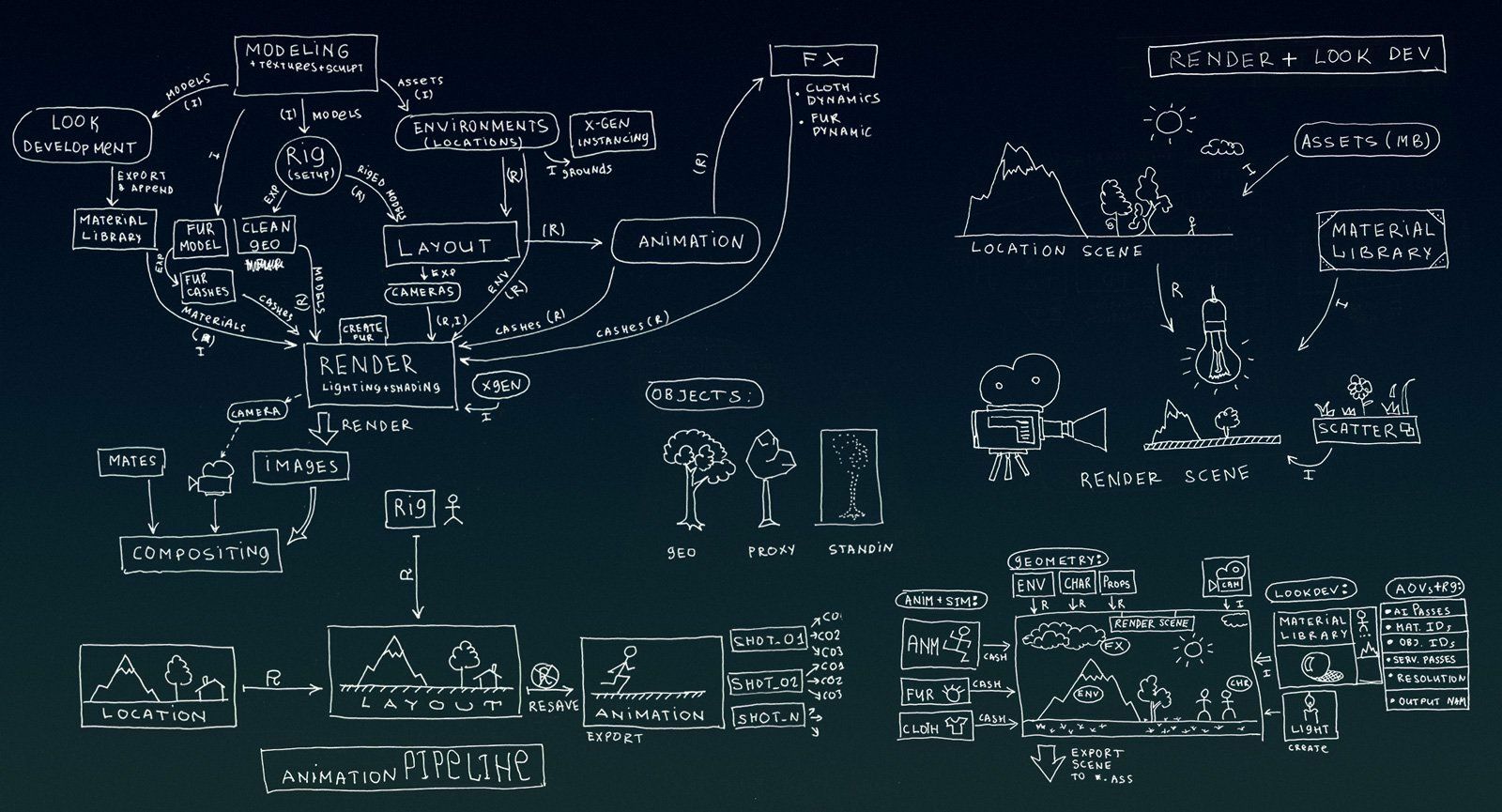
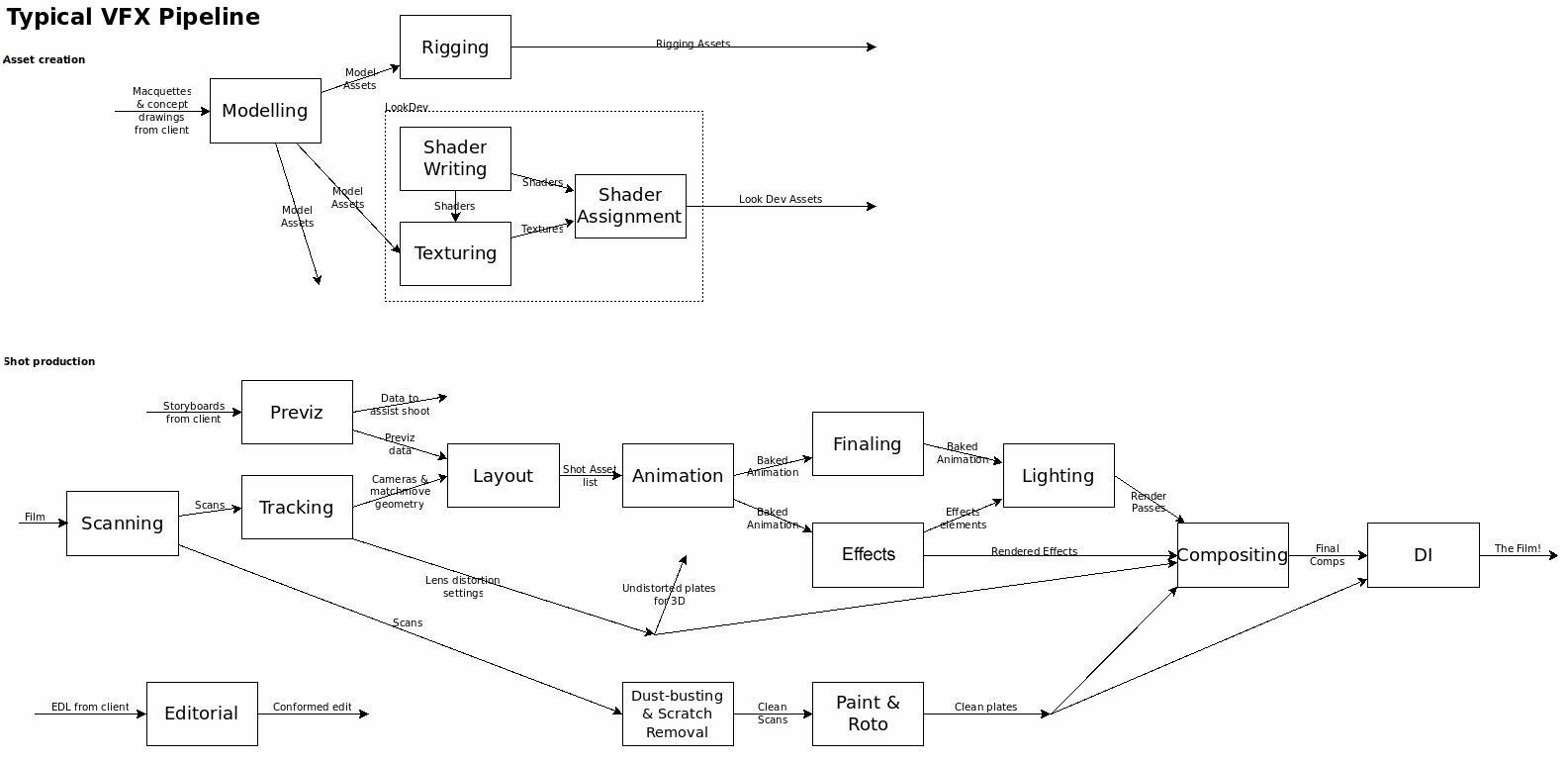
One of the most extensive and crucial aspects of CGI is 3D Modeling.
While 3D models make up the bulk of an environment, many backgrounds are still created using matte painting.
Scene preparation covers a number of processes, but they all serve the same purpose: prepare the provided footage for elements to be inserted in. Among these are motion tracking, rotoscoping and keying, and color correction.
Explosions, water, and smoke are all simulation-based effects that come to fruition here.
Texturing is the process of adding a surface color and texture to the 3D models, making them recognizable and now near completion.
One of the most important factors in realistic CGI is the fidelity of its lighting.
Compositing is the step often showcased in VFX reels, where everything comes together to assemble the completed product.
Example
Anyway, each project is different and unique.
For example, here is a short description of our working process in creating 3D product videos.
Steps
Step 1. Create the first draft
We do 2D draft render based on 2d images, to approve: - timings - composition - music (optional)
Parallel - we do 3d modeling if needed.
Step 2. Incorporate edits
We approve 2d animatic and move to a 3D part of the job
Step 3. 3D previz
We do 3d renders in draft quality
Step 4. Incorporate new edits
We approve the camera movement, timings, animation of the objects in the scenes
Step 5. Texturing and Render
We work on the textures, final look of the video - after approval, we start to render scenes
Step 6. Final
The final stage is compositing, we do final touches in compositing software and do final delivery
You can ask for a list of changes on every step.
Useful links
https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1218627/FULLTEXT02